Classification
| # of variables | # of modes | # of jumps |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Type | Continuous dynamics | Guards & Invariants | Resets |
|---|---|---|---|
| hybrid | non-linear polynomial | non-linear polynomial | identity |
Download
| Flow* | nonholonomic.model |
Model description
A simplified version of the hybrid control for Brockett’s non-holonomic integrator is described by the following ODE.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ \left\{ \begin{array}{lcl} \dot{x} & = & u \\ \dot{y} & = & v \\ \dot{z} & = & x\cdot v - y\cdot u \end{array} \right. \]](https://ths.rwth-aachen.de/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d41ee61a6eac30f5cf1d80e31c72f26a_l3.png)
wherein ![]() ,
, ![]() are the control inputs defined by
are the control inputs defined by
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ u \ = \ \left\{ \begin{array}{ll} 1, & x^2 + y^2 \leq |z| \\ -x + \frac{2\cdot y\cdot z}{x^2 + y^2}, & x^2 + y^2 > |z| \end{array} \right. \]](https://ths.rwth-aachen.de/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4b8cb67654eac9f98a7b07e0fc2de830_l3.png)
![]()
Reachability settings
We consider the initial set ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
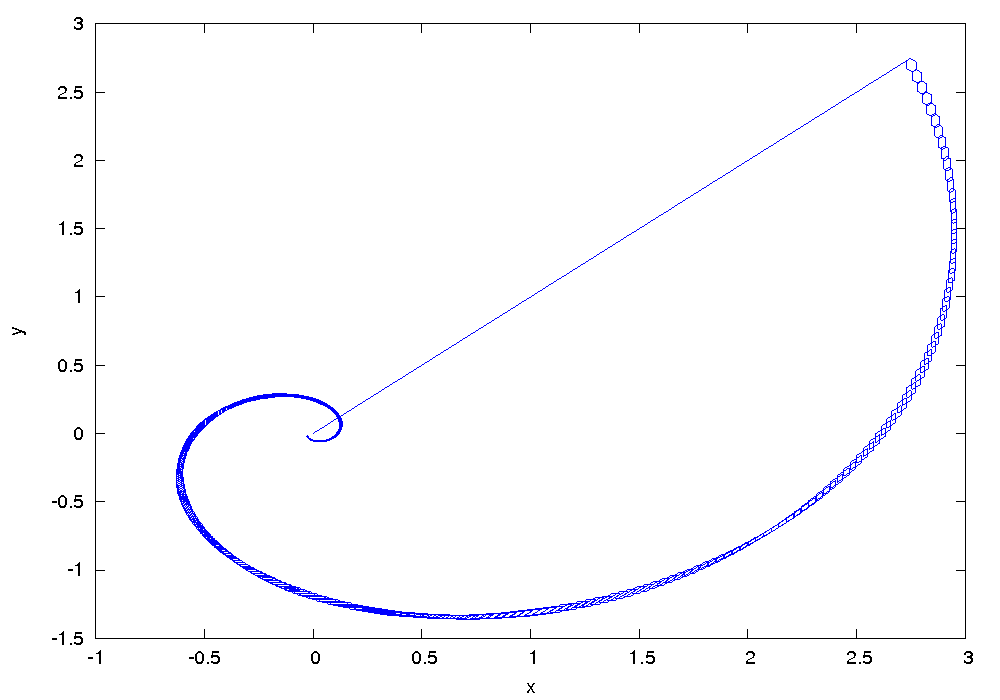
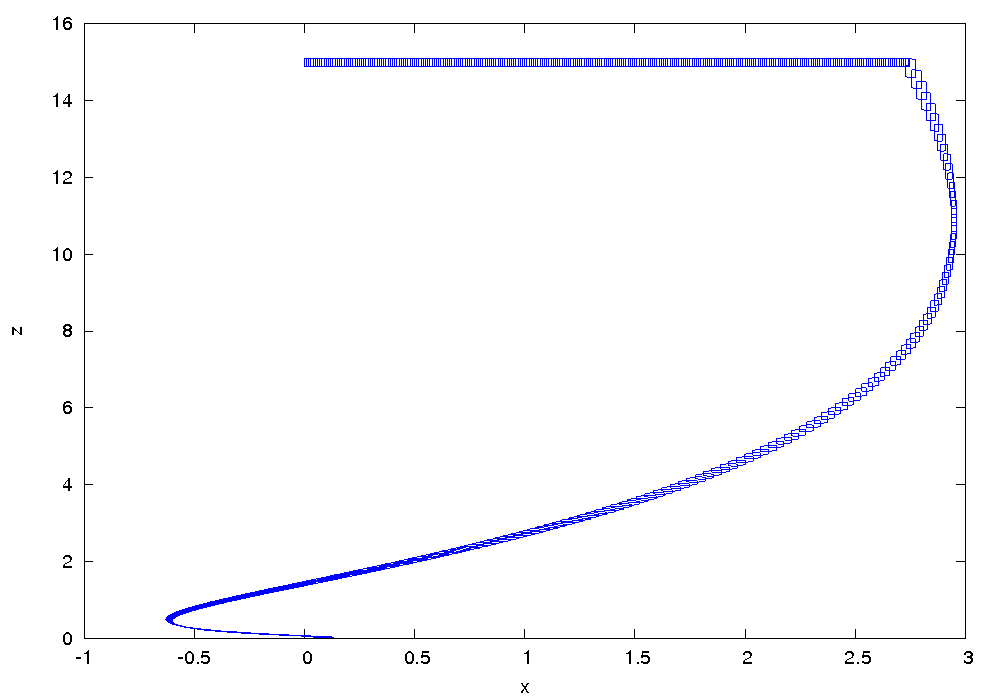
Results
The following figures show an over-approximation computed by Flow* for the time horizon ![]() :
: